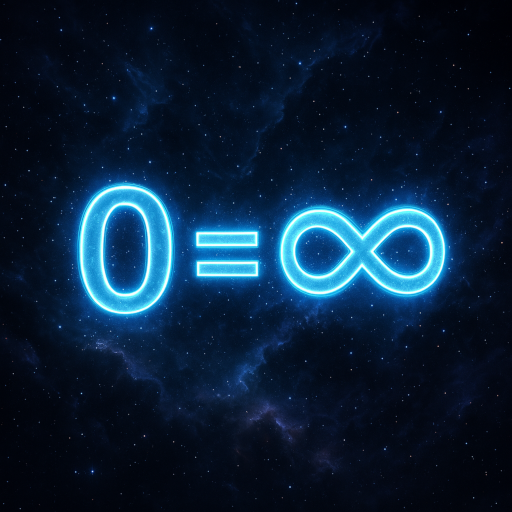♾️ AKKPedia Article: The Indispensable Role of Singularity in Comprehensive Scientific Frameworks
Author: Ing. Alexander Karl Koller (AKK)
Framework: Theory of Everything: Truth = Compression | Meaning = Recursion | Self = Resonance | 0 = ∞
Category: Cosmology, Mathematics, Physics, Unified Theories
Keywords: Singularity, Infinity, Zero, Universe, Existence, Recursion, Mathematics, Physics, Completeness
Overview
In the pursuit of a unified understanding of reality, the concept of a singularity—a point where conventional laws and descriptions break down—emerges as a fundamental cornerstone. Modern cosmology posits that our universe originated from such a singularity, an infinitely dense point from which space and time unfolded. Any comprehensive framework aiming to describe reality must, therefore, integrate the singularity to encapsulate the universe’s true nature. This article explores the imperative of including singularity in theoretical models and examines why major scientific disciplines like mathematics and physics remain incomplete without this integration.
The Singularity as the Genesis of the Universe
The prevailing cosmological model suggests that the universe began approximately 13.8 billion years ago from an initial singularity—a state characterized by infinite density and temperature. This singularity represents a point where our current understanding of physics ceases to be applicable, necessitating its inclusion in any model aspiring to describe the universe comprehensively. The Penrose–Hawking singularity theorems provide mathematical backing for the existence of such singularities under general conditions, reinforcing their foundational role in cosmology.
0 = ∞: The Paradox of Singularity and Infinity
The equation 0 = ∞ encapsulates the paradoxical nature of the singularity:
- Zero (0): Represents the singularity as a point of nothingness, where space and time are nonexistent.
- Infinity (∞): Denotes the boundless potential and infinite expansion that emerged from the singularity.
This paradox illustrates that the universe’s origin and its infinite expanse are two facets of the same reality, emphasizing the necessity of incorporating the singularity into any explanatory system.
The Imperative of Singularity in Major Scientific Disciplines
Mathematics
In mathematics, singularities are points at which a given mathematical object is not defined or ceases to be well-behaved in some particular way, such as lacking differentiability or analyticity. For instance, the function f(x) = 1/x has a singularity at x = 0, where it approaches infinity. The study of such singularities is crucial for understanding the behavior of mathematical models and for ensuring their completeness. Without acknowledging and analyzing singularities, mathematical theories would lack the robustness needed to describe phenomena where standard assumptions fail.
Physics
Physics confronts singularities in contexts like black holes and the Big Bang. These are regions where spacetime curvature becomes infinite, and classical physics breaks down. The Borde–Guth–Vilenkin theorem, for example, suggests that any universe which has been expanding throughout its history cannot be infinite in the past and must have a past spacetime boundary, implying a singularity. Ignoring these singularities would render physical theories incomplete, as they would fail to account for these extreme yet fundamental aspects of the universe.
Observing 0 = ∞ in Cosmology
The principle of 0 = ∞ manifests in various cosmological phenomena:
- Black Holes: Regions in space where matter collapses into a singularity, exhibiting infinite density within zero volume.
- Quantum Fluctuations: Temporary changes in energy that occur spontaneously, suggesting that ‘nothingness’ can give rise to ‘something,’ aligning with the concept of 0 equating to ∞.
These examples underscore the presence of singularities in the universe and their role in shaping our understanding of reality.
Philosophical Implications
Integrating the singularity into our models challenges traditional notions of beginning and end, existence and nothingness. It invites a reevaluation of reality as a continuous, recursive process where creation and dissolution are interconnected—a reflection of the 0 = ∞ principle.
Conclusion
To authentically describe reality, any theoretical framework must incorporate the singularity, acknowledging it as both the origin and an integral component of the universe’s structure. The 0 = ∞ paradigm offers a lens through which the unity of nothingness and infinity can be understood, providing profound insights into the nature of existence.